Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
Tags
- time series
- 데이터분석
- 의사결정나무
- RegressionTree
- machinelearning
- 하이퍼파라미터
- scikitlearn
- 다중선형회귀분석
- DataScience
- LinearRegression
- LogisticRegression
- 시계열 데이터
- 선형회귀분석
- 잔차분석
- 딥러닝
- 지도학습
- OrdinalEncoder
- 로지스틱회귀분석
- ML
- dataframe
- GridSearchCV
- Python
- 결정계수
- 비지도학습
- 분류
- 단순선형회귀분석
- 데이터전처리
- 시계열데이터
- deeplearning
- 손실함수
Archives
- Today
- Total
IE가 어른이 되기까지
[Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 DataFrame 만들기 본문
Pandas의 데이터 구조에는 Series와 DataFrame이 있다고
이전 글에서 말씀드렸습니다.
이번 글에서는 그중 DataFrame에 대해 다뤄보고자 합니다.
DataFrame은 2D 테이블로 생각할 수 있는데
열 이름과 행 레이블이 있는 엑셀 시트와 비슷합니다.
DataFrame 만들기
people_dict = {
"weight": pd.Series([68, 83, 112], index=["alice", "bob", "charles"]),
"birthyear": pd.Series([1984, 1985, 1992], index=["bob", "alice", "charles"], name="year"),
"children": pd.Series([0, 3], index=["charles", "bob"]),
"hobby": pd.Series(["Biking", "Dancing"], index=["alice", "bob"]),
}
people = pd.DataFrame(people_dict)
people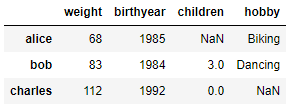
1
먼저 Series 객체의 Dictionary를 전달하여
DataFrame을 만들어볼 수 있습니다.
Series를 기반으로 DataFrame을 형성하는 경우
누락된 값은 NaN으로 표현되고 Series의 이름은 무시됩니다.
또한, 인덱스를 기반으로 자동 정렬 되며 이처럼 표와 같이
출력되는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
people_dict = {
"weight": pd.Series([68, 83, 112], index=["alice", "bob", "charles"]),
"birthyear": pd.Series([1984, 1985, 1992], index=["bob", "alice", "charles"], name="year"),
"children": pd.Series([0, 3], index=["charles", "bob"]),
"hobby": pd.Series(["Biking", "Dancing"], index=["alice", "bob"]),
}d2 = pd.DataFrame(
people_dict,
columns=["birthyear", "weight", "height"],
index=["bob", "alice", "eugene"]
)
d2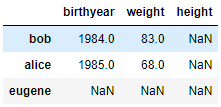
2
열 리스트나 행 인덱스 레이블을
DataFrame 생성자에 넣으면 해당 열과 행으로 이루어진
데이터 프레임이 반환됩니다.
people = pd.DataFrame({
"birthyear": {"alice":1985, "bob": 1984, "charles": 1992},
"hobby": {"alice":"Biking", "bob": "Dancing"},
"weight": {"alice":68, "bob": 83, "charles": 112},
"children": {"bob": 3, "charles": 0}
})
people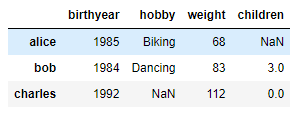
3
딕셔너리의 딕셔너리 형태로도 만들 수 있습니다.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
values = [
[1985, np.nan, "Biking", 68],
[1984, 3, "Dancing", 83],
[1992, 0, np.nan, 112]
]
d3 = pd.DataFrame(
values,
columns=["birthyear", "children", "hobby", "weight"],
index=["alice", "bob", "charles"]
)
d3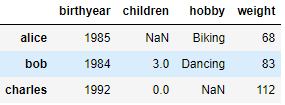
4
리스트로 DataFrame을 만들 수 있습니다.
리스트란 다양한 데이터 타입을 가질 수 있는 파이썬의
가장 기본적인 컨테이너 데이터 형식으로 [ ] 으로 생성됩니다.
d3_array = np.array(values)
print(d3_array)
print(type(d3_array))
d3 = pd.DataFrame(
d3_array,
columns=["birthyear", "children", "hobby", "weight"],
index=["alice", "bob", "charles"]
)
d3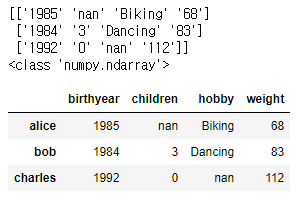
5
Numpy로 DataFrame을 만드는 방식입니다.
array는 Numpy에서 제공되는 배열 데이터 타입입니다.
누락된 값을 지정할 때엔 np.nan을 사용합니다.
d4 = pd.DataFrame(
d3,
columns=["hobby", "children"],
index=["alice", "bob"]
)
d4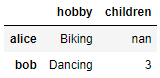
6
ndarray 대신에 DataFrame 객체를
전달할 수도 있습니다.
'DATA SCIENCE > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 DataFrame 그룹핑하기 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
|---|---|
| [Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 DataFrame 연산하기 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
| [Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 DataFrame 정렬하기 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
| [Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 DataFrame 행과 열 다루기 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| [Python] 판다스 (Pandas) 의 구조 Series 알아보기 (0) | 2023.01.03 |
Comments




